1890

1910

For more than 100 years, scientists have tested association and projective theories.
Read more1920

Colour association and colour preference testing are used to assess individuals.
Read more1947

Max Lüscher introduces the "Lüscher Color Test".
Read more1981

The birth of Colour Association Method merges the Lüscher Color Test with the word associations principle.
Read more1985
The pen and paper input diagnostics system is replaced by computers.
Read more1991

The switch from a text-based to a user-friendly graphic mode is made thanks to Windows.
Read more1995

Advances in computing allow for the creation of a more precise and user friendly CA method test system.
Read more2001

Increase in the use of CA method in guidance and counselling centres in the Czech Republic.
Read more2003

First online diagnostics
Read more2006

Establishing the evaluation head office, DAP Services, and creating the first products for education.
Read more2007
R&D for Human Resources
Read more2009
CA method is used in foreign languages for the first time.
Read more2011

R&D for marketing and sports.
Read more2012

Dispute in the Czech Republic with the Union of Psychological Associations.
Read more2013

A patent application.
Read more2014

CA method becomes an official diagnostics tool in Slovakia.
Read more2015

Establishing cooperation with Max Lüscher Institute.
Read more2016

DAP Services releases a CA method app for tablets.
Read more2018

R&D for health related fields, including the early diagnosis of dementia.
Read more2019

CA method continues to evolve along with advances in technology.
Read more2020

Adapting the diagnostics for use in a virtual reality environment.
Read more
1890
W. Wundt and W. James present new principles of conscious associations in humans.
Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt (1832 - 1920) explored mental actions (sensations, perception, emotions, ideas, associations, patterns), and how these elements are combined into more complex psychological activities. The laws of association were formulated on the basis of his experiments. (The first references to association theory were recorded at Aristotle.)
“William James (1842 - 1910) developed an original theory of emotions, which was similarly formulated at the same time by Danish physilogist Carl G. Lange. This theory is based on the assumption that emotional experiences are a response to physical changes caused by emotionally significant stimuli. Therefore, first there is a physiological reaction, which is followed by an emotional experience.”
Quote from https://wikisofia.cz/wiki/William_James

1910
For more than 100 years, scientists have tested association and projective theories.
Word Association Test
The Word Association Test is one of the oldest psychodiagnostic methods. More than 100 years ago, word associations were experimented with by Francis Galton, the methodology was elaborated upon by Wilhelm Wundt, and it was later introduced in psychopathology using Emil Kraepelin's methods. However, the practical use of this method is linked to Carl G. Jung, who in 1911 started using a standardized list of 100 stimulus words. During its lifetime, the WAT has undergone many modifications, and has changed methods of administration, evaluation, and interpretation.
The WAT can be used in both experimental studies and psychoanalysis. Test results show behavioural patterns, along with the possibility of understanding of a person's experiences. It achieves this by examining characteristics of speech.
Thought processes are reflected in the characteristics of speech. Therefore it is possible to understand an individual through the pace, conciseness, or depth of thought, in their speech. By extension, it is possible to identify possible disorders. The use of the WAT test can also be valuable for analyzing a person's interests and attitudes. This test is useable from early childhood through adulthood. It has no restrictions.
Sentence Completion Tests
In 1897 the Sentence Completion Test (SCT) was used by Hermann Ebbinghaus as part of an intelligence test that he defined as the ability to combine and integrate. However, Alexander Tendler pioneered the practical use of SCT in personality anaysis. This method can be implemented in various ways. All implementations rely on the same principle: the assessed person is supposed to complete unfinished sentences with the first thought that comes to their mind.
There are many different ways for SCTs to be used, and they can be designed for a specific purpose. Generally, they are used for clinical needs, in screening and research. Their evaluation is usually qualitative. However, some of the more sophisticated versions meet psychometric criteria. The Rotter Test (Rotter Incomplete Sentences Blank, 1950) has three forms: High School, College and Adult. The split-half reliability of the test reached the value of r = 0.83. The validity of the test was also confirmed with its ability to distinguish between adapted and non-adapted individuals. The Curtis Completion Form (James W. Curtis, 1953) is designed to evaluate emotional maturity and adjustment. This test is evaluated on the basis of content analysis and was standardised using a group of 335 people. The biserial correlation coefficient for distinguishing between normal and neurotic subjects was r = 0.97, between normal and abnormal r = 0.98 and between neurotic and psychotic subjects it was r = 0.73. Test The SCT (Joseph M. Sacks and Sidney Levy) contains 60 unfinished sentences divided into 15 categories, with 4 sentences in each category. Categories may include a person's relationship with one's mother, father, or family, one's abilities, or their past and future. The result of the multiple conformity assessment in 1,500 people was 92%. 72% of the findings from the test were consistent with the existing clinical diagnosis.
Rorschach Test
The Rorschach Test is a projective test. The author of the Rorschach Test is Swiss psychologiest Hermann Rorschach, who sought to evaluate personality through ink blotts. Detailed information on this method is available at https://www.rorschach.org.

1920
Colour association and colour preference testing are used to assess individuals.
Colour preference-based methods are a type of manipulation method, during which an individual chooses, then transforms or manipulates stimulus material. Projective manipulation methods are used in the psychoanalysis of children and adults. Among the most famous of these tests are the Lüscher Color Test (LBT, 1949) and Mas Pfister's Coloured Pyramid Test (BPT, 1946), in which both authors based their assumptions on the fact that individual behaviour towards colour is related to personality, and especially affectivity. Pfister's test is not only about choosing colours, but also about their arrangement. Lüscher's test, however, evaluates the importance of the preference for and rejection of specific colours. The hypothesis behind the tests is that colour preference is dependent on personality variables, the body's situational condition, and objective factors (Svoboda, M.: Psychologická diagnostika dospělých/Psychoanalysis of Adults, Prague, Portál 1999). The theory behind the tests is that there is a relationship between physiological mechanisms and colour structure. For example, a certain colour is linked to specific forms and contents of an individual's behaviour and experience.
Another so-called colour test is the Chromatic Association Experiment (CAE), developed by Vadim Ščepichin in the 1970s. This method is specifically for analysing personality characteristics and defining an individual's social relationships, including one's personal value system. The testing material in the original version of the CAE test consists of 12 coloured crayons and a list of dozens of stimulus words. According to the author the test was designed to represent the reality of life as much as possible, and fall into the cognitive, emotional and social category. The CAE test is a projective, or semi-projective, personality test, more recently known as the Test of Colour Semantic Differential (TCSD, Ščepichin, Ricklová). The framework of the technique is close to that of the colour association tests in that it also works with colours as a means of analysis, and uses procedures typical for assessment scales (Osgood's Semantic Differential). To start with, an individual has to allocate three appropriate colours to each stimulus word, and then numberically rate each word on a scale of 1-4. Finally, they should sort the colours hierarchically in order of personal preference. The method is based on comparing the individual levels of the stimulus words' evaluation. Instead of using the general psychological meaning that each colour is traditionally asigned, the authors of the TCSD based the test on the meaning given to the colour by each individual. The authors admit that individual colours evoke a specific emotional response in people that is similar throughout the majority of the population. The test measures a word's subjective meaning by having 3 colours assigned to it out of a possible 12 (unconscious rating), and using a 1-4 scale (conscious rating). The evaluation and interpretation process works with the relationship between the stimulus words that were created using association chains. Variables, such as color hierarchy, color combination within the hierarchy, and color frequency in the log, are monitored. During evaluation the stimulus words are rated on a 4-point scale and divided into 4 categories: unambiguously preferred, rather preferred, rather declined, unambiguously declined. Qualitative analysis is an integral part of evaluation and interpretation. The test is used in the psychoanalysis of children as well as adults.

1947
Max Lüscher introduces the "Lüscher Color Test".
Professor Dr Max Lüscher (1923 - 2017), known to the public for his Color Test, died on 2nd of February 2017 in Lucerne, aged 93. He was born in Basel, where he studied sociology, philosophy and clinical psychiatry. He first presented his Color Test at the World Congress of Psychology in Lausanne in 1947. His book “Lüscher-Color-Diagnostik” was published in 1949, and was gradually translated into 27 languages. In the same year, Max Lüscher earned his doctorate in philosophy and psychology at the University of Basel. The Lüscher Color Test has been used clinically since 1947. (Source: Max Lüscher Institute) www.luscher-color.ch
Max Lüscher was also the head of the Institute of Psycho-Medical Diagnostics in Lucerne (Switzerland). He went on to become a professor in Amsterdam and lectured at universities in Paris and Rome, Yale University in the USA, in South America, at universities in Western and Eastern Europe, and in Australia. (Max Lűscher Institute) www.luscher-color.ch
Over 40 studies dealing with the Lüscher Color Test are available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed

1981
The birth of Colour Association Method merges the Lüscher Color Test with the word associations principle.
Psychologist Jiří Šimonek was born in Krnov, Czech Republic where he studied at the local grammar school. He continued his education at the College of Social and Legal Studies in Ostrava, after which he studied psychology at Olomouc University. In 1977 he graduated as a single-field psychologist.
From the very beginning of his studies in psychology he took an interest in projective techniques and colours, which lead him to learning about the original Lüscher Color Test. He began using the Lüscher Color Test with children and youths while working at an educational and psychological counselling centre. In 1980, while working with the Lüscher Color Test, Jiří Šimonek realised that he wanted to garner more from the results than the test allowed. He aimed for perfection.
During his search for something that could give him better diagnostic tools, he attended a seminar on semantic differential. This seminar was inspiring, but still did not give him a more holistic approach to patient diagnostics. He felt that established diagnostics systems seemed too simplistic, even misleading. After a year of further research, he came up with the idea of merging the Lüscher Color Test with the word associations principle, creating the seed for CA method. CA method links the knowledge of the basic principles of associations in human consciousness with colour preference measurements, allowing Šimonek to focus on a person in their entirety.

1985
The pen and paper input diagnostics system is replaced by computers.
The initial version of Colour Association Method involved the clinician showing someone colourful squares, while they filled in words on paper. It took approximatley six hours per test to evaluate the data acquired in this way. Then in 1985 CA method was moved from a pen and paper system to a computer. 1985 proved to be a milestone year allowing for greater amounts of data to be acquired and evaluated, thereby further improving the method.

1991
The switch from a text-based to a user-friendly graphic mode is made thanks to Windows.
The first version of the CA method's evaluation programme was created at the end of the 80s on a Consul computer. With the arrival of Windows in 1991 it moved from text mode into a distinctly more graphic and user-friendly mode.

1995
Advances in computing allow for the creation of a more precise and user friendly CA method test system.
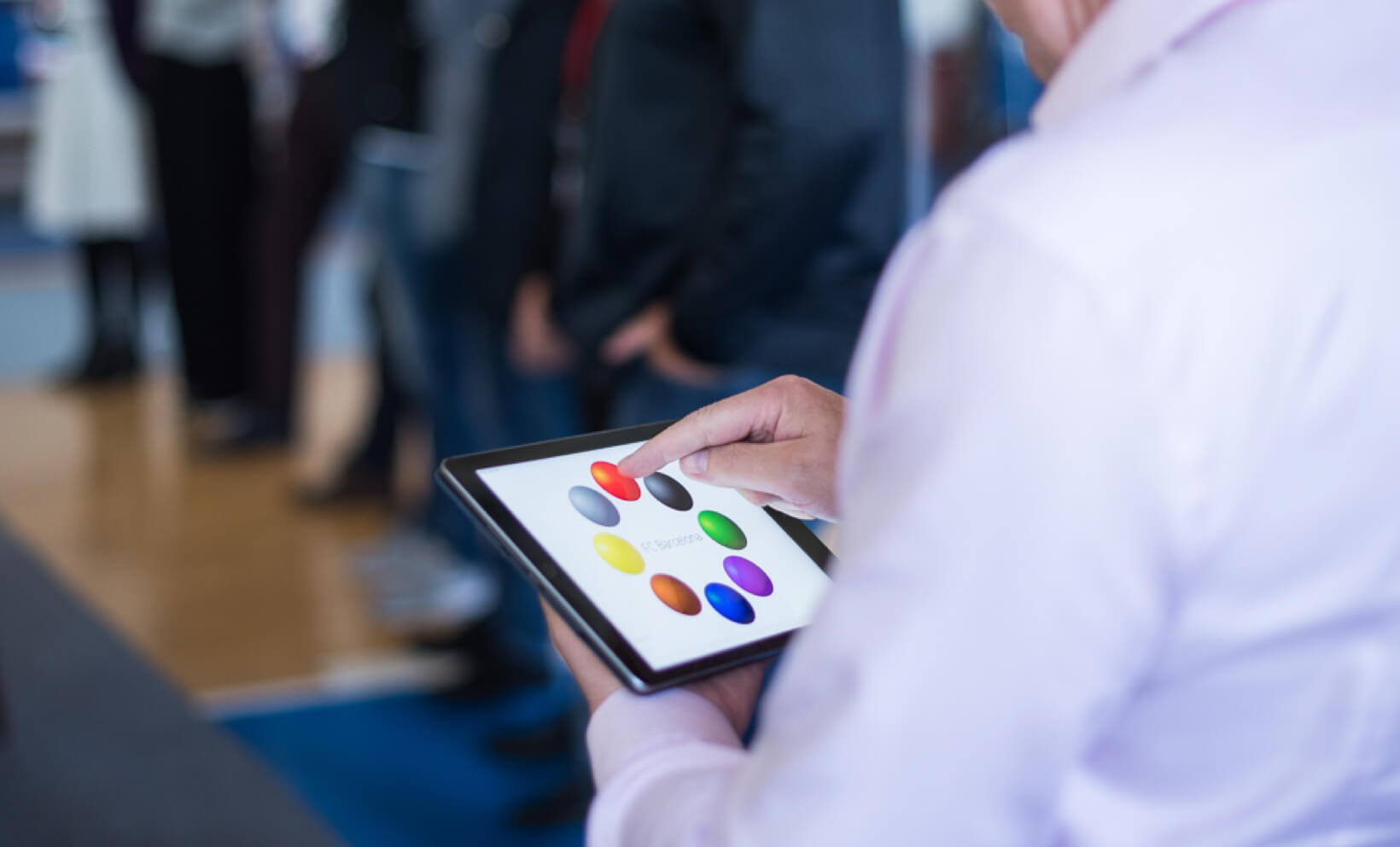
In the 90s technological advancements allowed for numerous changes to CA method's diagnostics system. Among the most significant changes were making the diagnostics test possible to take from home, and creating a more precise visual component for the test. It was in 1995 that it first became possible to seperate the data collection process from the evaluation, allowing the diagnostics to be carried out at a person's home. After completing the test at home, an individual could then either post or email their data for evaluation. The modification of the Method's visual component (associating words with colours) played a significant role in making the diagnostics process more pleasant, and the results more accurate. To do this, the original squares were replaced by simulated colourful balls. Each ball contains one colour, but instead of being a flat single-colour, the colour is presented as a gradient giving the ball a 3D appearance. The word object was then placed inseide a circle of colourful balls. These improvements were made possible by a team of IT experts including Jiří Šimonek, David Šimonek, Daniel Holešínský, Robert Bohoněk, and Petr Slavík.

2001
Increase in the use of CA method in guidance and counselling centres in the Czech Republic.
By 2001 CA method had been used by enough people that it began to gain attention across the Czech Republic, once there was a significant number of people who had used the method. Users were primarily educational and psychological counselling centres, but there was also a rising demand for the training of specialist advisers and consultants.

2003
First online diagnostics
The massive growth of the internet in 2003 brought with it another leap forward – the first online diagnostics. By bringing the diagnostics online, the last barreier between the test centre and the clients was removed.

2006
Establishing the evaluation head office, DAP Services, and creating the first products for education.
DAP Services was founded in 2006 with the aim of introducing CA method to a global audience. A group of four programmers, led by Jiří Šimonek, designed and implemented a comprehensive and robust technological online solution, that was prepared to host the CA method's international evaluation centre. The DAP Services team has been working on the implementation of the system in multiple languages, and the integration of the diagnostics into other fields. A team of specialists in psychology, sociology, programming, management, and marketing was set up in order to focus on the research and development of CA method, and its application to all areas of human life. The first products focused on education were created. To learn more about CA method in education, click here.

2007
R&D for Human Resources

2009
CA method is used in foreign languages for the first time.
2009 was the first year when the method was used in a foreign language. Over the next ten years, it was adapted for use in 32 more languages (e.g., English, German, French, Italian, Russian, Spanish, Portuguese, Hebrew, Chinese, Polish, Dutch, Arabic, Swedish, etc.). From this point on, the use of the method has largely shifted abroad. CA method becomes a global diagnostic platform and the Czech Republic is only one of the 30 countries in the world where the method is used. By that time, more than 50 new products that use CA method had also been created thanks to the cooperation with more than 250 business partners from all over the world.

2011
R&D for marketing and sports.

2012
Dispute in the Czech Republic with the Union of Psychological Associations.
In 2012, CA method had to deal with criticism from the Union of Psychological Associations (UPA) in the Czech Republic, which resulted in a lawsuit.
The UPA argued that there was an insufficient theoretical basis for CA method. Due to this, the UPA also concluded that it was impossible to validate the theory, and that the theory was lacking reliability. They also noted a lack of manuals, and detailed procedures for working with clients. DAP Services countered that the lack of evidence for CA method was due to its early stages of development, and early stages of use within education, HR and sports.
DAP Services believes the other points of the UPA's argument to be false and deliberately damaging to the name of the Method and the company. The UPA's criticism fuelled a media based campaign against the Method and DAP Services, further damaging the Method. At the time of the dispute CA method was called Barvy Života/Colours of Life.
DAP Services filed a lawsuit against the UPA for its defamation. Following the resignation of the anti-campaign initiators from the UPA in 2013, the litigation was closed and terminated by agreement of both parties.
DAP Services considers presenting the theoretical outcomes of CA method to be one of several priorities that include continuing to study CA methods validity and reliability as a diagnostic tool. Scientists and specialists from around the world are aleady using, testing, and validating CA method. For more information about the studies that CA method is involved in, click here.

2013
A patent application.
In 2013, a patent application for CA method was submitted. The patent application contained an exact calculation of a sample parameter from the input data to the output, in the same way as individual parameters are prcoessed in the computer kernel. The full patent application is available here.
The system and method of a computer-based market research analysis
Identification: US 20140067475 A1
Translators: ŠIMONEK, JIŘÍ, ŠIMONEK, JIŘÍ, BOHONĚK, ROBERT AND OTHERS
Name of the owner: DAP SERVICES A.S., CZECH REPUBLIC
Abstract
A market research computer implemented method for evaluating correlation between an entity and concepts associated with the entity. First, the method includes sending from a database, to many users data indicative of the entity and the concepts. Next, repeatedly performing for each user: collection of data indicative of sub-group of color selections, from a predefined group of colors, for both the entity and the concepts. Next, creating a data structure representing Color Association (CA) profiles respectively for each concept of the specified concepts by aggregating of sub-groups of colors selections by the users in respect of the concepts. Next, creating a data structure representing a Color Association (CA) profile for the entity by aggregating sub-groups of color selections by the users in respect of the entity. Next, calculating correlation between a CA profile of the concepts and the CA profile of the entity and reporting on the correlation results.

2014
CA method becomes an official diagnostics tool in Slovakia.
CA method was one of seven methods included in Komposyt (www.komposyt.com) the national Comprehensive Guidance System in Slovakia. Furthermore, two products based on CA method have been developed and standardized for use in the national education, and guidance systems. Following the standardisation, 300 psychologists were trained to work with and implement the Method.
CA method has become part of the European Centre for Development of Vocational Training (CEDEFOP) “Handbook of Transferability”, which is a guide “for transferability of practices” for projects implemented within the EU.

2015
Establishing cooperation with Max Lüscher Institute.
In 2015, DAP Services established a cooperation with the Max Lüscher Institute. Both teams agreed that there are only a few academic studies proving the validity and reliability of both methods, and in 2015 they decided to fill this gap together. The objective of the partnership is to improve the quality of the existing publications, and strengthen the validity and reliability of both methods. The Max Lüscher team especially appreciated the DAP Services team's modern approach in the field of IT solutions and technologies, in which, despite many years of effort, Lüscher-Color-Diagnostik AG has not achieved their digital goals.

2016
DAP Services releases a CA method app for tablets.
CA method is becoming the foundation for diagnostics and intervention solutions in the psychological preparation of athletes. The diagnostics system is tablet-friendly. Consultants, who work with the results from the diagnostics, have gone through several days of training and professional supervision. To learn more about CA method in sport, click here.

2018
R&D for health related fields, including the early diagnosis of dementia.
A year-long scientific study has shown the suitability of using CA method for detecting the early stages of dementia. Scientists from the Czech Republic and the United Kingdom examined CA method’s usability in relation to healthy adults, and adults with either neurological or physical defects. A study focusing on this subject was published in July 2017 in Healthcare Technology Letters.

2019
CA method continues to evolve along with advances in technology.
In concepts that include artificial intelligence, the consultant (human) is replaced by a virtual friend (buddy), who can interpret the results of the diagnostics, and based on the results help the respondent with appropriate advice or tips on what behaviour to change in order to better perform in life.
The virtual friend is visualized in an online form and, in the first phase, is managed by decision trees that learn from our empirical knowledge that is based on the framework of consultants' interventions from the last 25 years. These decision trees allow a virtual friend to decide which actions and advice to give to the respondent.
A virtual friend operates within an internet browser, or within an app on a smartphone. Within the application we will collect feedback from users, from which we will evaluate the relevance and functionality of the recommendations the virtual friend gives to the respondent. We will then improve the virtual friend's behaviour using the respondents' feedback.
Introduction of artificial intelligence
While operating the above applications, we will receive enough data to enable us to apply artificial intelligence to the diagnostic tool. With the applicaiton of AI to CA method, the computer will be able to look for connections that we would not find empirically. Subsequently, it will assist the virtual friend in learning to make better decisions and to behave more accurately. The result is a more effective form of assistance to the respondent. Newly found algorithms will be automatically applied to the applications, and the applications will themselves learn to work better.

2020
Adapting the diagnostics for use in a virtual reality environment.
CA method diagnostics can be performed in a simulated 3D environment using a stereoscopic imaging device in the form of a headset (3D glasses) and two peripherals containing position sensors. The result of the diagnostics is also displayed in 3D virtual reality immediately after the completion of the diagnostics.